Backend rules
The configuration of so-called Backend Rules represent the next step in the set-up of the Rule Engine. In VRMT we consider Backend Rules as the basic set of directions that we provide to enrich XML source files with useful information about the company's IT environment. Also, Backend Rules are static rules, that is, they provide a sort of static mapping table against which incoming attributes are added up with other pieces of information.
In contrast to the Rule Manager (discussed in the ensuing section) Backend Rules do not offer conditional transformations. The rather basic set of directions simply instructs VRMT on how to treat incoming technical information like IP addresses, operating systems, etc. with respect to the corporate IT network. IP addresses and IT environments are a case in point. Let's say, we know that generally all IPs ranging from 53.30.131.00 through 53.30.131.49 are PROD systems, whereas the remainder up until 53.30.131.99 belong to DEV systems. In this example we would configure Backend Rules to assign PROD and DEV environment labels to XML alerts for these respective IP ranges.
 Note: proper role authorization is required to view, edit or change any data within this module. In case you do not see the described module please approach your system administrator or authorization contact.
Note: proper role authorization is required to view, edit or change any data within this module. In case you do not see the described module please approach your system administrator or authorization contact.
How to customize static rules in Backend Rules
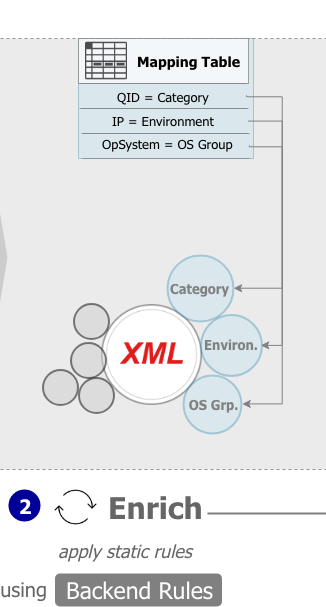
![]() To access the Backend Rules click on the respective button in the left navigation bar. The Backend Rules represent the interface used to configure static enrichment rules in order to classify XML files according to attributes like IT environment, OS groups, Qualys category, and location.
To access the Backend Rules click on the respective button in the left navigation bar. The Backend Rules represent the interface used to configure static enrichment rules in order to classify XML files according to attributes like IT environment, OS groups, Qualys category, and location.

Upon opening Backend Rules the initial center screen is blank. To invoke existing attribute mapping tables click on the right-hand drop-down box and make a selection. You have the following options:
- Category by Qualys ID
- Environment by IP
- Environment by IP Net
- Location by IP Address
- OS Group by OS
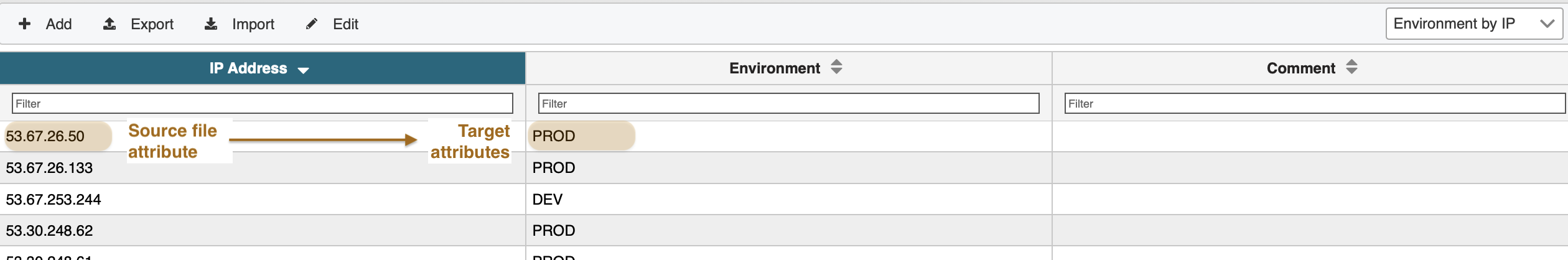
When clicking on Environment by IP a mapping table opens that allows you to create a 1:n mapping of source attributes to target attributes. In above example, if the source field IP Address contains the value "53.67.26.50" the system will write the "PROD" to the target field Environment.
 Please note: while values in the column IP Addresses need to be unique, the values in the Environment column need not.
Please note: while values in the column IP Addresses need to be unique, the values in the Environment column need not.
Backend Rules comprise various convenient ways to manipulate mapping rules. Depending on your needs you have the option to either add, edit or remove single values or adapt many values with a comfortable bulk edit option.
Adding single mapping values
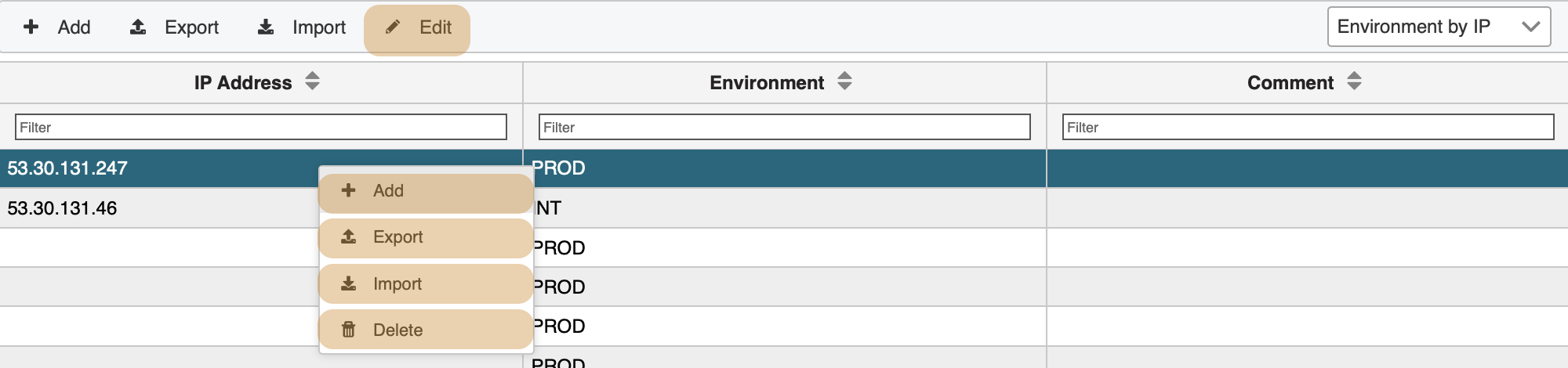
If you require to add single values hit the + Add button on the top left of the header panel. Alternatively, secondary or right-click on a row value will give you a context menu. A popup screen opens ready to add additional mapping values.
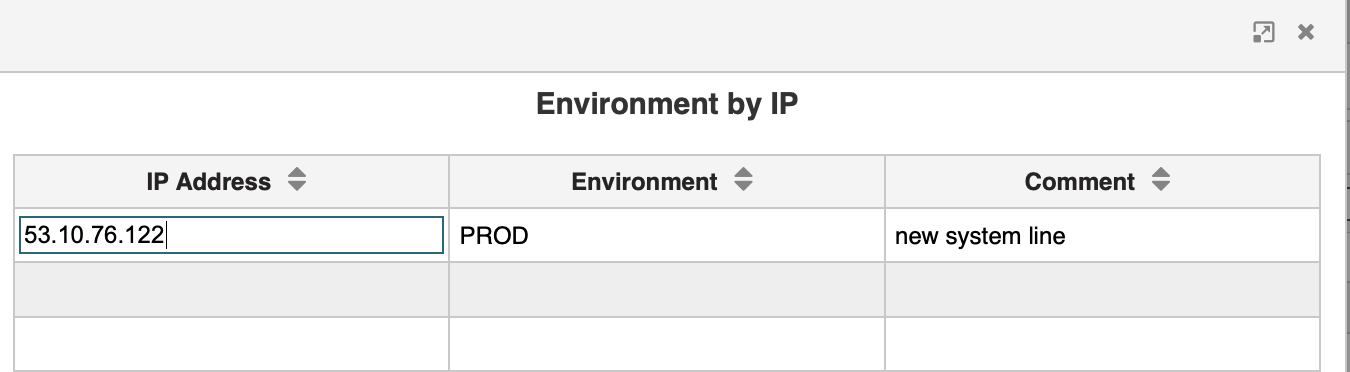
You enter the source value in the left column and enter a corresponding mapping value in the middle column. Should you require an explanatory note you may enter a textual description in the comment column. When done, save you additions by clicking the confirmation button on the bottom right.
Changing single mapping values (direct table edit)
To alter existing single values the screen provides you with a comfortable direct table function. That is, you may change table values directly in the table in the way you see them. This is in particular helpful in cases where you need to quickly correct individual values. To do, so hit the Edit button on the top header panel. The table is now editable directly.
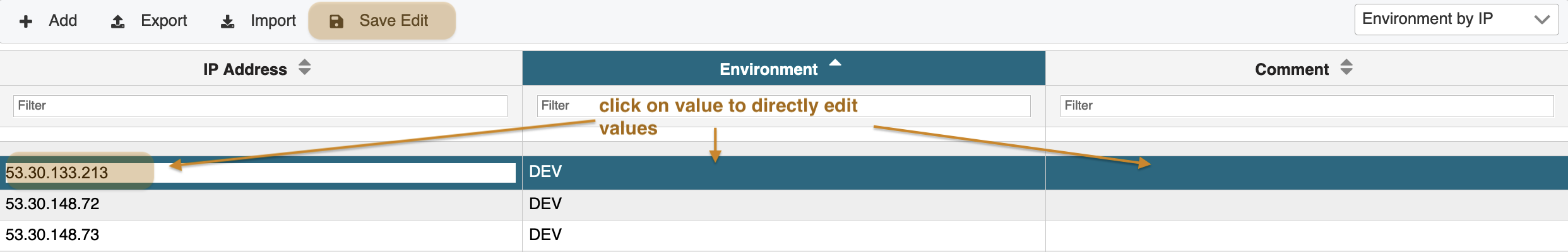
Click on a row value and change the attribute value. When finished confirm your changes by clicking Save Edit on the header panel.
Deleting single mapping values
Removing single values works a bit differently. Highlight a row and invoke the context menu by right-clicking. Clicking Delete removes the entire row.
Bulk editing mapping values (export / import)
More often than not you will, however, need to manage myriad combinations of source/target values and execute regular adaptions. Bulk editing empowers you with a handy export / import feature that allows you to download the mapping tables and re-upload them once you are done with your changes.
To download the table click on Export (header panel or context menu). You will receive the table as a spreadsheet download. Once you are finished with you changes, you may import the spreadsheet using the Import function.
 Caution: the import function generally overwrites existing values and will not check for existing values. You will overwrite the whole rule set by your uploaded data set. Be sure that you have chosen the right data set for the rule set.
Caution: the import function generally overwrites existing values and will not check for existing values. You will overwrite the whole rule set by your uploaded data set. Be sure that you have chosen the right data set for the rule set.
updated on: 5/9/2019 ⏐updated by: Wolfgang Stoettner ⏐ v1.0.1
